在业务供应链中,代理、经销商或分销商的使用十分常见。代理、经销商或分销商(即第三方/中介)通过向客户销售产品或提供服务赚取佣金。
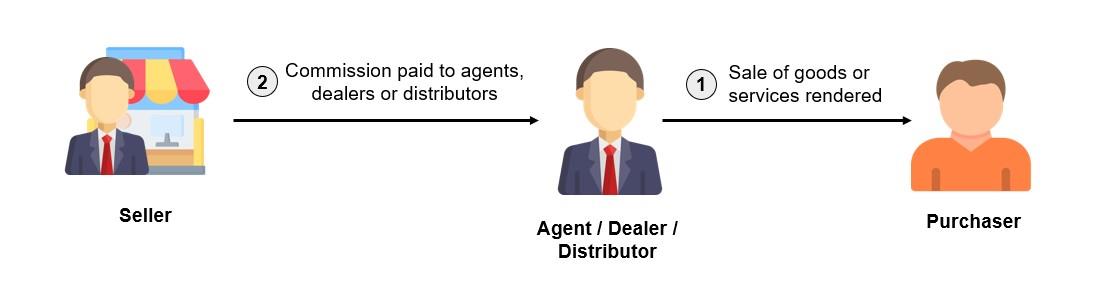
图1.1 涉及代理、经销商或分销商的业务概览
卖家向购买者开电子发票
-
当商品或服务通过代理、经销商或分销商购买时,电子发票的处理流程是什么?
-
- 卖方必须向购买者开电子发票以记录交易。
- 如果购买者未要求电子发票,卖方需开具普通收据。在月末,卖方必须在七个日历日内将这些收据合并为一张电子发票,作为收入证明。
- 开电子发票的详情可以参阅 电子发票指南第3.5和3.6节.
买家向代理,经销商或分销商开自发电子发票
-
当代理、经销商或分销商从卖方获得佣金或奖励时会发生什么?
- 卖方需要开自开电子发票,以记录支付给代理、经销商或分销商的佣金或奖励。这符合《1967年所得税法》第83A条的规定。
- 电子发票的开具流程详见电子发票指南第2.3和2.4节。
-
在自发电子发票的场景中,谁是
-
- 供应商:代理、经销商或分销商
- 购买者:卖方(作为费用证明开具自开电子发票)
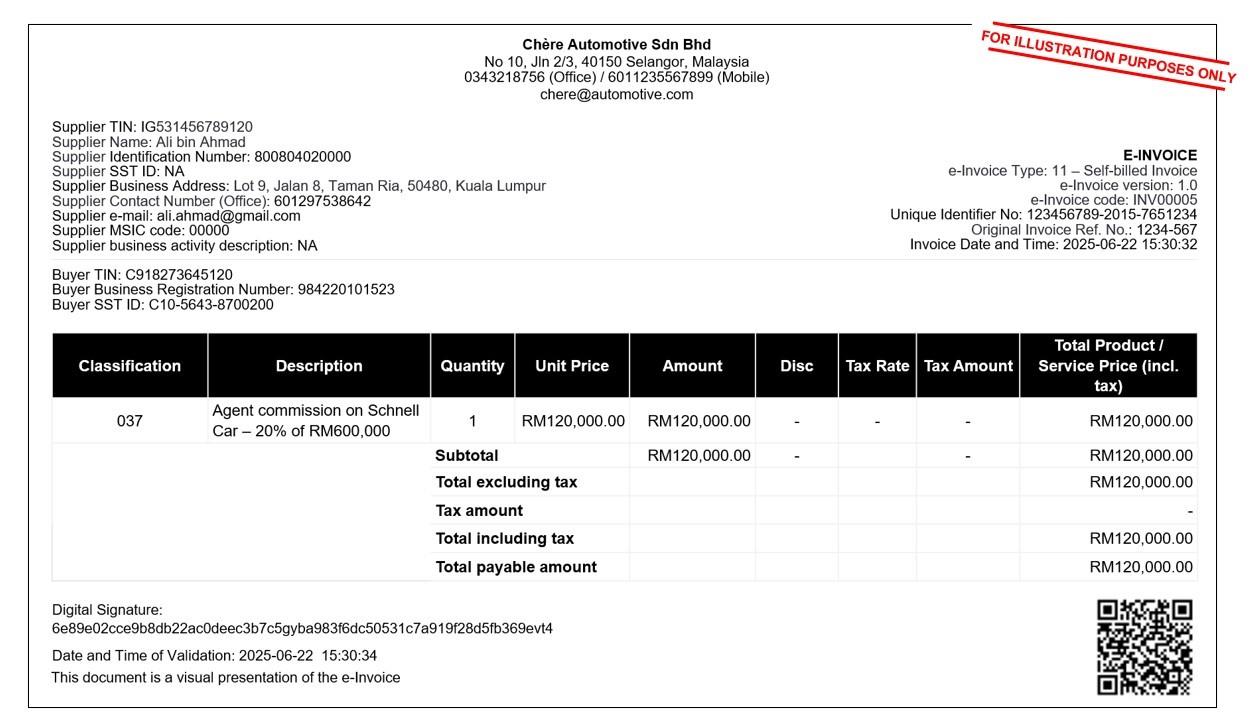
图1.2 企业向其代理开具自开电子发票的流程示意图
你可以通过参考大马税务局(IRBM)发布的官方指南,进一步了解电子发票的机制和流程
你也可以考虑参与《电子发票战略课程》来获得详细与最新的资讯。
欲了解更多有关电子发票与课程详情,请点击此网址: ANCGroup_E-Invoice Courses Contact.
ANC Group – Your Personal Tax Advisor
Tax consulting is the core service of ANC Group. Our tax professionals provide clients with comprehensive tax support and guidance. We offer tax consulting and compliance services for expatriates, entrepreneurs, and listed and non-listed companies.
Our tax consulting services include business tax, transaction tax, personal tax, and corporate income tax. We don’t just guide you in interpreting and applying complicated taxation rules, but to explore new opportunities and business trends.
ANC Group keep you abreast with Malaysia tax updates and any changes in the local regulations.
We work closely with industry specialists, authorities, and associated professionals within ANC Group to provide the best-in-class integrated tax planning solutions. ANC specialists coordinate the accounting and taxation services to bring your business to success.







