read this in PDF
Measures under Covid-19 and Restriction of Movement Order (18.03.2020 – 31.03.2020)
- Background
- Essential Services
- Non Essential Services
- Manufacturers
- Deadlines for Tax Filing
- Tax Estimate for Affected Industries
- Royal Malaysian Customs Department deadline
- FAQ by Ministry of Human Resource
- Employment Retention Program (RM600 / month)
Covid-19 Movement Control Order
Essential Services
Background – Movement Control Order
The Covid-19 pandemic has been declared a pandemic by the World Health Organization which impacted people’s lives in most countries. Malaysia is no exception. To prevent further spread of the virus, the Malaysian Government has decided to implement a nationwide Restriction of Movement Order beginning 18 March to 31 March 2020.
1.Prohibition on mass movements and gatherings, including religious, sports, social and cultural gatherings. All business premises shall be closed, except supermarkets, public markets, grocery stores and convenience stores selling daily necessities.
2.Prohibition on Malaysians from travelling abroad. Malaysian returning home are required to undergo health checks and voluntary self-quarantine for 14 days.
3.Prohibition on entry of tourists and foreign visitors into Malaysia.
4.Closure of all kindergartens, government departments and private schools.
5.Closure of all public and private higher education institutions and skills training institutes.
6.Closure of all government and private premises. Exceptions are allowed for premises providing essential services.
Kindly note that the definition of essential services read out by the Prime Minister during the announcement defers from the Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases (Measures within the Infected Local Areas) Regulations 2020.
| Essential Services | ||||
| Banking & Finance | Electricity and Energy | Fire | Port, Dock and Airport Services and undertakings | Postal |
| Prison | Production, refining, storage, supply and distribution of fuel and lubricants | Healthcare and medical | Sold waste management and public cleansing | Sewerage |
| Radio communication including broadcasting and television | Telecommunication | Transport by land, water or air | Water | E-commerce* |
| Defense and security | Food supply | Wildlife | Immigration | Customs |
| Hotels and accommodations* | Any services or works determined by Minster as essential or critical to public health or safety | |||
*newly added
Non Essential Services
Manufacturers in Critical Industries
Non Essential Services
Clarification was given through a Media Release issued by the National Security Council of Malaysia in which Non Essential Services were added to the list:
| Non Essential Services | |||
| Motor Vehicle Repair | Towing Services | In-Progress Construction | Funeral Arrangement |
Even though non-essential services above were permitted to operate, businesses should adhere to the rules and regulations which may imposed by the local authorities. For example the Majlis Perbandaran Shah Alam only allows motor vehicle service provider to operate until 2.00 p.m.
Critical Industries
The Ministry of Industry and International Trade (MITI) held an engagement session with Federation of Malaysian Manufacturers (FMM), National Chamber of Commerce and Industry of Malaysia (NCCIM), American Malaysian Chamber of Commerce (AMCHAM) and Japanese Chamber of Trade and Industry, Malaysia (JACTIM) which represent the country’s manufacturing sector. Kindly refer to the official guidelines HERE.
The government recognizes the importance of certain critical goods and goods which are essential to the supply chain, hence such industries are allowed to operate. However special rules are imposed:-
1.Company must reduce the number of workers to the minimum or at least 50%;
2.Company must meet the demand and need for product or service for the local market;
3.Company must submit MITI the list of involved workers and ensure the movement of workers is restricted from home to business premise;
4.Company must provide temperature screening and take daily temperature readings of employees;
5.If temperate is found abnormal, Company must contact nearest health office or government hospital;
6.All workers must comply Covid-19 preventive procedures issued by Ministry of Health from time to time;
7.Company must provide hand sanitizers at the entrance and other relevant places, and make sure workers wear a face mask.
8.Company carries out disinfection process at the premise before each shift or operation begins;
9.Sanitization and cleaning process should be carried out 3 times a day;
10.Company must ensure employee’s transport undergoes a sanitation and disinfection process before use;
11.Companies must ensure social distancing best practice guidelines are in place;
12.In the event a worker being infected with Covid-19, company is responsible for the full costs of medical, disinfecting and other relevant costs;
13.The government emphasizes that the approval can be cancelled or revoked if Company fails to meet specified conditions;
14.Government reserves the right to amend the above condition.
Guidelines for Income Tax Filing
Registration and Payment of Tax

Tax Filing Due Date Extension under Restriction of Movement Order
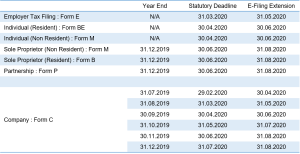
Kindly refer to E-filing Program by IRB HERE.
Tax Estimate for Affected Industries
Affected Industries
Malaysian companies are required to pay income tax in advance by way of a tax estimate (“CP204”). During the the Restriction of Movement Order, companies are asking whether they can defer their tax estimate instalment?
The clear answer is “No”, unless you fall within the affected industries.
Relaxation is given to affected industries such as tourism, hotel operators and airlines. These affected companies are allowed to revise their tax estimate, as long their 3rd revision month falls within year 2020. For example, companies with December Year End, can revise their 3rd month tax estimate by April 2020, a special extension of time given by the IRB,
Withholding Tax, RPGT and CbCR
Withholding Tax and Real Property Gain Tax
Withholding tax and Real Property Gain Tax (RPGT) which is due during the Restriction of Movement Order will be extended to 30 April 2020.
Country-by-Country Reporting (CbCR)
Submission of CbCR which is due by 31 March is also given an extension of time to 30 April 2020. Kindly refer to the detail Frequently Asked Question (FAQ) HERE.
Indirect Tax under RMCD
Extension of Time for submission under Royal Malaysian Customs Department (“RMCD”)
Submission of return which is due by 31 March 2020, which includes Sales Tax, Service Tax and Tourism Tax will be given an extension of time till 15 April 2020. Kindly refer to RMCD announcement HERE.
Frequently Asked Questions by Ministry of Human Resource (MOHR)
FAQ in relation to Covid-19 Issues in Workplace & Movement of Control Order
The MOHR has issued a FAQ in relation to Covid-19 at the Workplace dated 19 March 2020.
1.What should the employer do if the employee is suspected or tested positive with Covid-19?
Employer needs to instruct all employees whom are working very closely with the infected employee to be self-quarantine for 14 days. In addition, the workplace including common area must be sanitized. Infected employee is also required to identify colleagues whom were very close to him/her.
2.Employee is given a quarantine notice under Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases Act 1988 for 14 days. What should the employer do?
Employer shall grant sick leave, including hospitalisation up to 60 days under the Employment Act 1955.
3.We are unable to continue our business and forced to take the measures below:-
a. Retrenchment
b. Voluntary Separation Scheme
c. Lay off
d. Pay cut
What should we do? Will the labour office take legal action against us?
In respect of the circumstances above, employer is required to inform such measures to the authority at least 30 days before such measures to be implemented. Refer this guideline.
Employer can also refer the Guidelines on Retrenchment Management (For Employers and Employees).
4.During the Movement Control Order period (18 March to 31 March 2020), can we deduct Annual Leave? Otherwise, is this Paid Leave or Unpaid Leave?
Employer cannot force employee to deduct Annual Leave. Annual leave has to be under application and will of the employee. During this period, it is a paid leave. For employees who are out of the scope of Employment Act 1955, and Labour Ordinance of Sabah and Sarawak, the employer is obliged to pay according to the employment contract agreed between both parties.
Employment Retention Program (ERP)
Employment Retention Program (ERP)
During the Covid-19 pandemic, employers went into a panic state with employees ordered to go under Voluntary Separation Scheme (VSS), Retrenchment or Unpaid Leave. The ERP shines as an immediate financial assistance of RM600 per month, for 6 months, provided for employees who have been instructed to take no paid leave by their employers who are economically affected.
Eligibility Conditions
1.All private sector employees including temporary employees who have registered and contributing to EIS;
2.Limited to employees with monthly salary of RM4,000 and below; and
3.Employers who have implemented no-pay leave (30 days minimum) for a period of 1 to 6 months, with no pay leave notice issued beginning 1 March 2020.
Application must be made by employers on behalf of their employees using Form ERPC-19, with effect from 20 March 2020.
The ERP payment shall be credited to the employers’ account and employers are required to credit the payment directly to the affected employees’ accounts within 7 days upon receipt of payment from SOCSO.





