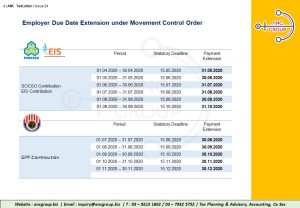
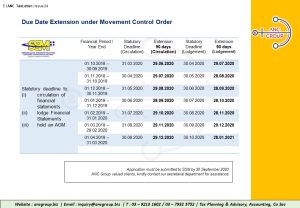
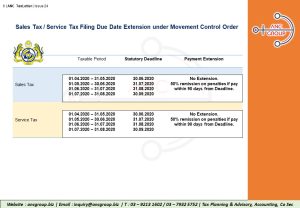
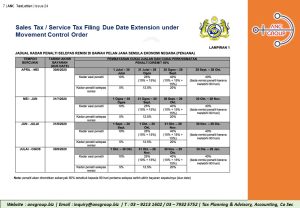
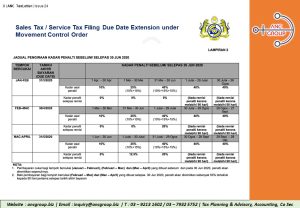
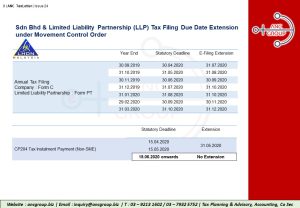
1. Extension of Statutory Due Dates

2. PENJANA Initiatives
Wage Subsidy Programme (WSP) 2.0
On 23 September 2020, Prime Minister Tan Sri Muhyddin Yassin announced that WSP will be extended for another 3 months. Under the WSP 2.0 :-
a.eligible for companies that are facing income loss of 30% or more compared to previous year;
b.companies must be registered with the Social Security Organisation (SOCSO) by 31 August 2020;
c.RM600 per employee for 3 months (up to 200 employees); and
d.companies which have never received WSP will be eligible for 6 months.
Hiring Incentive
Effective 1 July 2020, employers can apply for hiring incentive for newly recruited employee, subject to the following qualifying conditions:-
1.Employer must hire employee through : https://www.myfuturejobs.gov.my/
2.Employer must register hiring incentive through : https://penjanakerjaya.perkeso.gov.my/
| Hiring Incentive Amount | |||
| Apprentice | 40 years old and below | 40 years old and above / OKU | |
| Total | RM 600 / month | RM800 / month | RM1,000 per month |
Flexible Work Arrangement Incentives
1.At present, mobile phone and monthly bills paid by employer is exempted from tax. Under the PENJANA, it has been extended to include notebook and tablet received from employer. The exemption on perquisite is capped at RM5,000.
Effective 1 July 2020 (pending gazette).
2.Special individual income tax relief of up to RM2,500 for the purchase of mobile phone, notebook and tablet.
Effective YA 2020 (pending gazette).
Personal Tax Relief for Fees paid to Child Care Centre
At present, resident individuals can claim tax relief up to RM2,000 for child care fees paid to a registered child care centre and kindergarten, for child aged 6 years and below. It was proposed that the relief will be increased to RM3,000.
Effective YA 2020 and YA 2021 (pending gazette).
Tax Relief for COVID-19 Related Expenses
At present Personal protective equipment such as face masks and COVID-19 testing are deductible under Section 33(1) of Income Tax Act 1967 whereas capital expenditure incurred such as acquisition of thermal scanners can be claimed as Capital Allowance under Schedule 3 of Income Tax Act 1967.
Effective 1 March 2020 (pending gazette).
Special Tax Relief on Purchase of Mobile Phone, Notebook and Tablet
A special personal income tax relief of up to RM2,500 given to resident individuals for purchase of mobile phones, notebooks and tablets [pending further clarification from the Inland Revenue Board]. This special tax relief overlaps with the current lifestyle relief.
For purchases between 1 June 2020 to 31 December 2020 (pending gazette).
Special Tax Relief on Tourism Expenses
At present, a special personal income tax relief of up to RM1,000 given to resident individuals for domestic travelling expenses incurred between 31 March 2020 to 31 August 2020. The special tax relief has been extended to 31 December 2021.
The expenses eligible for tax relief includes accommodation fees and tourist attraction’s entrance fee.
Effective for YA 2020 (Travel dates between 1 March 2020 to 31 December 2020) and YA 2021 (pending gazette).
Special Tax Deduction for Renovation and Refurbishment of Business
At present, a special tax deduction is given for renovation and refurbishment of business up to a limit of RM300,000 for capital expenditure incurred during the period of 1 March 2020 to 31 December 2020. The special tax deduction has been extended to 31 December 2021.
Effective 1 March 2020 (pending gazette).
Accelerated Capital Allowance (ACA) on Eligible Capital Expenses
At present, qualifying capital expenditure incurred on ICT Equipment is entitled to Capital Allowance at the rate of :
Initial Allowance 20% | Annual Allowance 20%
Instead of Year of Assessment, it was proposed that the annual allowance is to be increased to 40% for capital expenditure incurred during period of 1 March 2020 to 31 December 2020. The ACA is to be extended to 31 December 2021.
Effective 1 March 2020 (pending gazette).
Income Tax Rebate for Newly Incorporated Small Medium Enterprises (SME)
RM20,000 income tax rebate for first 3 years of assessment is given to SME, subject to the qualifying conditions below:-
1.Incorporated under Companies Act 2016 ;
2.Paid up capital less than RM2,500,000 and annual turnover not exceeding RM50,000,000 ;
3.Tax rebate amount is equivalent to Capital Expenditure or Operating Expenses incurred in each year of assessment, up to a maximum of RM20,000 ;
4.Unutilized tax rebate is not allowed to be carried forward ;
5.It has to be a newly setup company, not a transfer of assets / business from an existing business; and
6.Other rules which may be imposed from time to time.
For SMEs incorporated and commenced its business operation from 1 July 2020 to 31 December 2021.
Effective 1 July 2020 (pending gazette).
Special Tax Deduction for Rental Discount given to SME Tenants
Landlords of business premises that offer rental discount to SME tenants from April 2020 to September 2020 are allowed to claim a special deduction equivalent to the rental discount subject to the condition that the discount is at least 30% of the existing rental rate. Salient points to take note include:-
| Eligible Person | Any taxpayers which include corporate, individual, cooperative or other business and non-business entities renting to any qualified SME tenants. | |||||||||
| Definition of SME |
SME that are eligible for this special tax deduction has to obtain SME Status Certificate from SME Corp Malaysia. Registration link : https://smereg.smecorp.gov.my/ |
|||||||||
| Supporting Documents | 1.Stamped tenancy agreement;
2.Rental income statement; 3.SME Status Certificate issued by SME Corp; and 4.Tenant’s information, rental information and rental deduction methods. A copy of the format can be found at : https://ancgroup.biz/smerentaldiscount/ |
Effective 1 April 2020 (pending gazette).
PRIHATIN Special Grant (GKP) 2.0 for Micro Enterprises
On 23 September 2020, Prime Minister Tan Sri Muhyddin Yassin announced that GKP will be reopen for fresh application. Eligible conditions are:-
a.a Malaysia citizen;
b.running micro enterprises with annual turnover less than RM300,000 and less than 5 employees;
c.business registered with IRBM / local authorities / SSM on or before 31 August 2020 (previously 31 December 2019);
d.active business at the time of application; and
e.first time applicant.
Register at https://gkp.hasil.gov.my/ starting 1 October 2020 to 31 October 2020.
Tourism Sector
1.Deferment of Instalment Payments
Businesses within the tourism sector are allowed to defer their monthly tax instalments for a period of six months from 1 April 2020 to 31 December 2020.
Effective 1 April 2020 (pending gazette).
2.Service Tax Exemption
Service Tax exemption is granted on accommodation services provided from 1 March 2020 to 30 June 2021.
Effective 1 March 2020 (pending gazette). Kindly refer to Service Tax Policy 9/2020.
3.Tourism Tax Exemption
The tourism tax will be fully exempted from 1 July 2020 to 30 June 2021.
Effective 1 July 2020 (pending gazette).
Stamp Duty Exemption for Home Ownership Campaign
Stamp duty exemption will be provided to residential properties which were acquired under the following conditions:
1.Sales and Purchase Agreement dated 1 June 2020 to 31 May 2021, signed between owner and developer (registered with REHDA, SHAREDA and SHEDA) ;
2.Discount given by developer is at least 10%; and
3.Buyer is a Malaysian Citizen.
Real Property Gain Tax (RPGT) Exemption for Disposal of Residential Property
Malaysian citizen who disposed his/her residential property between 1 June 2020 to 31 December 2021, is eligible for RPGT exemption. Limited to 1st three (3) properties.
The residential properties disposed cannot be acquired by way of a gift between family members under Paragraph 12 or No Gain no Loss under Paragraph 3(1)(b), Schedule 12 of RPGT Act 1976.
Effective 1 June 2020 (pending gazette).
Sales Tax Exemption on Passenger Motor Vehicles
It is proposed that 100% Sales Tax exemption is for Completely Knocked Down (CKD) passenger cars and 50% Sales Tax Exemption for Completely Built Up (CBU) passenger cars.
Effective 15 June 2020 to 31 December 2020 (pending gazette).
3. Practice Note Updates
Practice Note 2/2020 (dated 16 March 2020)
Claiming Capital Allowance on the Development Cost for Customised Software under Income Tax Rules 2019
The practice note was issued to provide guidance on the implementation of Income Tax (Capital Allowance) (Development Cost for Customised Computer Software) Rules 2019 [P.U.(A) 274/2019], which qualifies for the purpose of claiming Capital Allowance effective from YA 2018.
The qualifying expenditure for the purpose of claiming Capital Allowance under these rules consist of:-
1.Consultation Fee;
2.Payments for the Rights of Software Ownership; and
3.Incidental Fee.
It was clarified that such qualifying expenditure does not relief the taxpayers from its obligation to remit Withholding Tax for expenditure made to non-resident under s.109 or s.109B of the Income Tax Act 1967. Examples of such development cost were given under the Practice Note :-
|
Development Cost for Customised Computer Software Incurred |
Customised Computer Software is Capable of being used in Business |
Implication / Tax Treatment |
|
YAs 2018, 2019 and 2020 |
YA 2020 |
•Cost incurred from YA 2018 is a qualifying expenditure •Capital Allowance can be claimed from YA 2020 |
|
YAs 2017, 2018 and 2019 |
YA 2019 |
•Cost incurred from YA 2018 is a qualifying expenditure •Cost incurred before YA 2018 is disregarded •Capital Allowance can be claimed from YA 2019 |
|
YAs 2017 and YA 2018 |
YA 2018 |
•Only cost incurred from YA 2018 is a qualifying expenditure •Capital Allowance can be claimed from YA 2018 |
Practice Note 3/2020 (dated 18 May 2020)
Clarification on Determining the Gross Income from Business Sources of not more than RM50 million of a Company or Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
The practice note was intended to provide clarification pursuant to the amendment of the Income Tax Ac 1967 in regards to additional criteria applicable to a Company or LLP resident in Malaysia to be eligible for SME preferential rate of 17% and other relevant tax benefits.
|
No. |
Issues |
Implication / Tax Treatment |
|
1 |
Investment Holding Company (IHC) |
IHC under s.60F of the Income Tax Act 1967 (non listed IHC) is deemed to have no gross income from a business source hence not eligible for SME preferential tax treatment |
|
2 |
Company / LLP without gross income from businesses sources but have other income such as rent and interest (including temporarily closed business operations) |
It is deemed to have no gross income from a business source hence not eligible for SME preferential tax treatment. |
|
3 |
Company / LLP which has gross income from foreign business source |
Gross income from foreign business sources shall be taken into account in determining gross business income of RM50 million. |
|
4 |
Company/ LLP enjoying certain tax incentive such as Pioneer Status or Investment Tax Allowance |
Exempted gross income from business source shall be taken into account in determining gross business income not exceeding RM50 million. |
4. Operational Guidelines
Operational Guideline 1/2020 (dated 6 March 2020)
Procedure on Submission of Amended Return Form
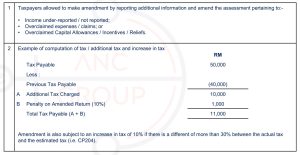
The guideline supersedes Operational Guideline 4/2019 dated on 30 August 2019 and aims to provide guidance to taxpayers who wish to make amendment to the information or assessment in their return forms (RF) by using Amended Return Form (ARF).
Operational Guideline 2/2020 (dated 12 May 2020)
Guidelines for Amendment of CP204 3rd month instalment falling in Calendar Year 2020 and Deferment of Tax Instalments
The guideline provides guidance for deferment of CP204 payments for normal companies and specific industries such as tourism. However, the guideline has not taken into account PENJANA initiative in which tourism sector has extended to cover tax instalment up to 31 December 2020.
Operational Guideline 3/2020 (dated 13 August 2020)
Guidelines on Imposition of Penalties
|
3/2020 |
Imposition of Penalties under :- a)s.112(3) of Income Tax Act 1967
b) s.51(3) of Petroleum Income Tax Act 1967
c)S.29(3) of RPGT Act 1976
|
5.International Tax
International Tax and Expatriate Residency Issues due to COVID-19 Travel Restrictions
In response to travel restrictions imposed due to the global COVID-19 Pandemic, the IRB has issued a FAQ and guidance to resolve the evolving situation. The salient points include:
1.Taxpayer currently outside of Malaysia due to COVID-19 Travel Restrictions. Will the absence affect his residence status?
The period of temporary absence from Malaysia due to COVID-19 Travel Restrictions shall be taken to form part of your period or periods in Malaysia for tax residence purpose. Proper documentation and records must be evidenced if IRBM requests.
2.Company unable to convene its Board of Directors meeting in Malaysia due to Travel Restrictions. Will this affect the Company’s residence status in Malaysia?
IRBM is prepared to presume the Company as a Malaysian resident , provided the Company is a resident in the immediate previous YA; and directors of the Company have attended the meeting held outside Malaysia (physically or electronically).
3.Cross Border Employment Income
Prior to Movement Control Order, taxpayer has been travelling in and out of Singapore to work. Due to Travel Restrictions, he can only temporarily work from home in Johor. Is the income taxable in Malaysia?
If there is no change in contractual terms governing employment overseas before and after return to Malaysia; and it is a temporary work arrangement due to Travel Restrictions, IRBM is prepared to accept the income not taxable in Malaysia. Subject to evidence and other conditions which may apply case to case basis.
6.Public Rulings Updates
Public Ruling (PR)1/2020
Tax Incentives for BioNexus Status Companies
PR 1/2020 supersedes PR 8/2018 to take into account Income Tax (Exemption)(No.2) 2009 (Amendment) Order 2018 and Income Tax (Exemption)(No.17) 2007 (Amendment) Order 2018.
The objective of this PR is to explain the tax treatment in respect of tax incentives for a BioNexus Status Company in Malaysia. BioNexus status is a special status awarded to qualified biotechnology companies undertaking value-added biotechnology or life sciences activities. A BioNexus status company would be able to enjoy fiscal incentives, funding assistance and other benefits to assist the growth of the Company.
The tax exemption is on statutory income from a new business or expansion project. The exemption period is ten (10) and five (5) consecutive YA respectively.
BioNexus status and tax exemption incentive is subject to the approval of the Ministry of Finance and registration can be done at www.bioeconomycorporation.my
Public Ruling (PR)2/2020
Tax Treatment of Stock in Trade – Valuation of Stock
Public Ruling (PR) 3/2020
Tax Treatment of Stock in Trade – Withdrawal of Stock
PR 2/2020 and PR 3/2020 supersede PR 4/2006. The PRs have been updated to take into account changes in accounting standards and amendment to Income Tax Act 1967. The salient points include:-
Value of closing stock at the end of a basis period :-
(a)is the market value at the end of the period; or
(b)amount equal to the total cost of acquiring the item (physically tangible stock). Any item of stock in trade consisting of immovable properties, stocks, shares or marketable securities, the value of these items at the end of the relevant period is an amount equal to its cost price or market value, whichever is lower.
Market value means price that stock would fetch if sold in a transaction between independent persons dealing at arm’s length. Replacement cost method to value stock in trade is not acceptable. Whereas for valuation of stock in trade at cost, first-in-first-out (FIFO) or weighted average cost formula are accepted. Last-in-last-out method is not acceptable for income tax purpose.
Accounting standards (MFRS 102 Inventories and s.13 of MPERS) provide guidance on valuation of stock which includes any write-down to net realisable value. However, reference to Para 7.3(b)(ii) of the PR, net realisable value is not acceptable for income tax purposes. Therefore, adjustments must be made in the tax computation to bring the valuation of stock in trade to comply with the requirements of the Income Tax Act 1967. Practically, it would posts a huge challenge to taxpayers and tax agents to rectify.
Valuation of stock in trade withdrawn for own use has to be :-
(a)accounted for as if the item of stock in trade had been sold; and
(b)Value at the market value at the time of its withdrawal and treated as gross income of the person
Effective from YA 2014, Section 4C of the Income Tax Act 1967 was introduced to provide gains or profits from a business shall include an amount receivable arising from stock in trade parted with by element of compulsion including on requisition or compulsory acquisition. The stock in trade will include movable and immovable goods. Clarification has been given in the case of a property development business, whereby the land is the stock in trade, any compensation received for the compulsory acquisition of the land would be treated as gross business income under Para 4(a) of the Income Tax Act 1967.
Public Ruling (PR)4/2020
Tax Treatment of any sum received and a Debt Owing that arises in respect of Services to be Rendered
Effective from YA 2016, amendment to Section 24(1)(b) of the Income Tax Act 1967 provides that where in a relevant period, a debt owing to a relevant person arises in respect of any services to be rendered (previously : any services rendered) in the relevant period or in any following basis period, the amount of the debt would be treated as gross income and bring to tax. Clarification has been given in this PR:-
(a)Debt owing to a person is defined as a contractual obligation to pay;
(b)Advance payment received for services to be rendered will be taxable;
(c)Refundable deposit and security deposit refundable upon completion of service, do not form part of the abovementioned provision;
(d)Treatment of Section 24 does not apply to income under Section 4A in relation to services provided by non-resident person; and
(e)Section 24(1)(b) and Section 24(1A) are not applicable to services that are governed by separate income tax rules, for instance, services provided under a construction contract or property development.
Public Ruling (PR)5/2020 、6/2020
Tax Treatment of Research and Development Expenditure :
– PR Qualifying Research and Development Activity
– Special Deductions
PR 5/2020 and PR 6/2020 supersede PR 5/2004. These PR should be read together with Guidelines on the Application Procedure for a Special Deduction in respect of a Qualifying Research and Development Activity dated 13 August 2020. You can refer to the Technical Guideline : here.
The qualifying condition can be summarise in the flowchart below:-
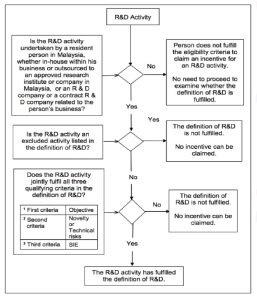
First Criteria – Is the objective of the R&D to:-
(a)Acquire new knowledge;
(b)Create new products or processes; or
(c)Improve existing products or processes.
Second Criteria:-
Does novelty exist in the newly acquired knowledge, or new and improved existing products and processes? Is the newness the first of its kind in Malaysia?; or
Is there an involvement of technical risks in achieving the desired outcome due to scientific or technological uncertainties that cannot be resolved by a competent profession in the relevant field?
Third Criteria:-
Was the R&D activity carried out using a systematic, investigative and experimental approach to resolve a scientific or technological uncertainty which is not readily deducible?
PR 6/2020 explains the R&D activities incurred can be claimed as:
(a)Special provision under s.34(7) (single deduction); or
(b)Special deduction under s.34A (double deduction); or
(c)Special deduction under s.34(B) (double deduction).
Kindly refer to each qualifying condition in the PR : here.
7.Service Tax Policies Updates
Service Tax Policy1/2020
Expansion of Scope of Taxable Service
Effective 1 January 2020, First Schedule of Service Tax Regulations 2018 has been amended by Service Tax (Amendment)(No.2) Regulations 2019 to widen the existing taxable service. Such effected groups include:
Group G :
a)provision of IT service expanded to include distributing or reselling of IT services on behalf of any person;
b)provision of electronic medium that allows suppliers to provide supplies to customers; and
c)provision of digital services including transaction of digital services on behalf of any person.
Group I :
a)provision of telecommunication service expanded to include digital service; and
b)provision of advertising service include digital advertising service.
Service Tax Policy 1/2020 (Amendment 1)
Effective 14 May 2020, Group G (b) above has been widen to include digital services provided on behalf of any person, but clarified to exclude services in relation to matters outside Malaysia.
Service Tax Policy 2/2020
Service Tax Exemption on Imported Taxable Service
Effective 1 January 2020, registered person is granted exemption on imported taxable service, with the following qualifying conditions:-
a)the person is a registered person and accounted service tax;
b)provide same services to customers as imported taxable service;
c)for furtherance of business;
d)has paid amount payable for the imported taxable service to the service provider; and
e)taxable services under Group G [exclude item (j) and item (k)] / advertising services under Group I, item (8).
The Service Tax Policy also explains the service tax treatment in regards to transitional periods.
Service Tax Policy 3/2020
Claiming a Refund by Offsetting Method on Service Tax on Imported Digital Service provided by Foreign Registered Person
Effective 1 January 2020, local service provider who has paid Service Tax to Foreign Registered Provider (FRP) on imported digital services is allowed to claim a refund granted under Section 34(3)(b) of the Service Tax Act 2018 by offsetting method. The qualifying conditions are:-
a)the person is a registered person under the Service Tax 2018;
b)provide the same digital service as the imported digital service;
c)for furtherance of business;
d)Imported digital service provided by a FRP under Service Tax 2018; and
e)Payment of Service Tax has been made to FRP.
The local service provider can claim the refund by declaring the actual amount of Service Tax paid to FRP via Form SST-02, item 13(c).
Service Tax Policy 3/2020(Amendment 1)
Clarify on typographical error on Foreign Service Provider and Foreign Registered Provider (dated 13 August 2020).
Service Tax Policy 4/2020
Service Tax on Online Distance Learning Services
Service Tax Policy 4/2020(Amendment 1)
The amendment is to clarify digital services provided by both local and foreign service providers are subject to Service Tax.
Effective 1 January 2020, online distance learning services include preschool education; primary and secondary education; and tertiary education are exempted.
Service Tax Policy 5/2020
Service Tax on Online Newspaper, Online Journals and Periodicals
Service Tax Policy 5/2020(Amendment 1)
The amendment is to clarify digital services provided by both local and foreign service providers are subject to Service Tax.
Effective 1 January 2020, online newspaper, online journals and periodicals are exempted.
Service Tax Policy 6/2020
Provision of Training and Coaching Services for Disable Person
Effective 1 January 2020, training services or coaching services provided to a person who holds a valid OKU Card issued under the Persons with Disabilities Act 2008 are not subject to Service Tax provided the service provider is a training and teaching centers:-
a)registered with Ministry of Health of Malaysia;
b)registered with Social Welfare Department; or
c)registered by any national association for persons with disabilities registered with the Registrar of Societies Malaysia.
Service Tax Policy 7/2020
Accounting of Service Tax for Persons Exempted from Payment of Service Tax under Item 3 and Item 4, Service Tax (Persons Exempted from Payment of Tax) Order 2018
Effective 1 January 2020, recipients of the imported taxable service under item 3 or item 4 of the Service Tax (Persons Exempted from Payment of Tax) Order 2018, shall not be required to pay service tax.
Item 3 : Any person who acquires digital services from foreign registered person
Item 4 : Information technology service acquired from any person who is outside Malaysia
Service Tax Policy 8/2020
Group Relief Facility on Provision of Taxable Services to Company within the Same Group of Companies
Provision of specific services under Group G, First Schedule, Service Tax Regulations 2018 to any person in the same group of companies is not a taxable service. Effective 1 January 2020, group relief facility is enhanced whereby group relief is granted even though taxable service is provided to a third party, subject to the condition the value of taxable service does not exceed 5% of the total value of taxable service within twelve (12) months.
Service Tax Policy 8/2020(Amendment 1)
The amendment provided clarity to taxable service provided by company within the same group of companies outside Malaysia, such service shall not constitute an imported taxable service. Where a company is a FRP provides any digital service to any company in Malaysia within the same group, such digital service shall not subject to Service Tax.
Service Tax Policy 9/2020
Service Tax Exemption for Group A : Accommodation [Economic Stimulus Package 2020]
Accommodation premise operator such as hotel operator is exempted from Service Tax from 1 March 2020 to 31 August 2020.
Service Tax Policy 9/2020(Amendment 1)
The exemption period has been extended to 30 June 2021.
Service Tax Policy 10/2020
Service Tax Exemption on Provision of Digital Services related to Banking / Financial Services
Effective 1 January 2020, Ministry of Finance has decided that digital services related to banking / financial services provided by local service providers, is not subject to Service Tax under s.34(4) of the Service Tax Act 2018. Local service providers granted exemptions are:-
a)Banks, investment banks or financial institution licensed under the Financial Services Act 2013, Islamic Financial Services Act 2013, the Labuan financial Services and Securities Act 2010, and the Labuan Islamic Financial Services and Securities Act 2010.
b)Development Financial Institutions prescribed under the Development Financial Institutions Act 2002 or other written law.
8.Income Tax Gazette Orders
Gazette Order P.U. (A) 363
Income Tax (Exemption) (No. 13) 2005 (Revocation) Order 2019
The Income Tax (Exemption) (No. 13) Order 2005 [P.U.(A) 102/2005) which exempts non resident company from payment of income tax on income received from an approved MSC status for technical advice, licensing fee in relation to technology development and interest on loans for technology development, will be revoked from 1 January 2020.
Gazette Order P.U. (A) 274
Income Tax (Capital Allowance) (Development Cost for Customised Computer Software) Rules 2019
In conjunction with Budget 2018, effective YA 2018, development cost for customised computer software is eligible for claiming Capital Allowance. The development cost includes consultation fee, payment for rights of software ownership and incidental fee relating to the development of customised computer software.
Gazette Order P.U. (A) 387
Income Tax (Deduction from Remuneration) (Amendment) Rules 2019
In conjunction with Budget 2020, effective YA 2020, chargeable income band / non-resident individual taxpayer’s income tax rate be increased from 28% to 30%. The Gazette Order takes into account the 30% tax rate in the Monthly Tax Deduction (MTD) calculation.
Gazette Order P.U. (A) 398
Income Tax (Deduction for Expenditure Incurred for Provision of Approved Internship Programme) Rules 2019
Tax Incentive for Structured Internship Programme / Approved Internship Programme has been proposed since Budget 2015, but has not been gazette until 31 December 2019. The Gazette Order explains the qualified person and qualified courses. It is deemed to be effective from the YA 2015 to YA 2021.
Gazette Order P.U. (A) 399
Income Tax (Exemption) (No. 3) 2014 (Amendment) Order 2019
Angel investor is granted tax exemption in respect of his/her aggregate income in the second YA following the YA in which the investment is made. In conjunction with Budget 2020, the application period for an angel investor for an angel investor to submit an application is now extended to another 3 years until 31 December 2023.
Gazette Order P.U. (A) 414
Income Tax (Exemption) (No. 8) (Amendment) Order 2019
Gazette Order P.U. (A) 415
Income Tax (Deduction for Payment of Educational Loan of Perbadanan Tabung Pendidikan Tinggi Nasional (PTPTN) by Employers on behalf of Employees)
Employer is eligible to claim tax deduction on the PTPTN repayment amount paid on behalf of his Malaysian employee. The employee who received such perquisite is exempted from personal income tax. The exemption and deduction is extended to YA 2021.
Gazette Order P.U. (A) 30
Income Tax (Exemption) (No. 9) Order 2019) (Amendment) Order 2020
Tax exemption is given on employment income for a maximum of 12 consecutive months to women who return to work after a career break. This incentive is eligible for applications received by Talent Corporation Malaysia Berhad from 1 January 2018 to 31 December 2023 (previously 31 December 2019).
Gazette Order P.U. (A) 139
Income Tax (Exemption) Order 2020
The Minister exemptions religious institution or organization in the basis period for a YA from payment of tax in respect of gross income from all sources. Subject to conditions imposed by Minister. An application shall be made to the Director General on or after 1 January 2020. Effective YA 2020.
Gazette Order P.U. (A) 141
Income Tax (Exemption) (No.2) Order 2020
The Minister exempts qualifying company from payment of income tax in respect of statutory income derived from a qualifying project. The qualifying project referred to:-
a)Business providing healthcare services at a new private healthcare facility; or
b)Project of expansion, modernization or refurbishment of the existing business of providing private healthcare services.
Effective YA 2018.
Gazette Order P.U. (A) 153
Income Tax (Exemption) (No.3) Order 2020
The Minister exempts an individual from payment of income tax in respect of withdrawal from a Private Retirement Scheme (PRS) by the individual before reaching age 55. The PRS must be contracted under s.139Q of the Capital Markets and Services Act 2007, for the period from 30 April 2020 until 31 December 2020. The maximum withdrawal amount exempted is RM1,500.
Gazette Order P.U. (A) 172
Income Tax (Exemption) (No. 8) 2017 (Amendment) Order 2020
Gazette Order P.U. (A) 173
Income Tax (Accelerated Capital Allowance)(Automation Equipment) 2017 (Amendment) Rules 2020
Manufacturing Company is eligible for Accelerated Capital Allowance on capital expenditure incurred in the purchase of automation equipment. In conjunction with Budget 2020, the tax incentive has been expanded to:-
Category 1 : Labour intensive industries à extended for another 3 years until YA 2023.
Category 2 : Other industries à extended for another 3 years until YA 2023
In Budget 2020, it is also proposed that the scope of incentive under Category 2 be expanded to services sector, but this has yet to be gazetted.
Gazette Order P.U. (A) 237
Income Tax (Special Treatment for Interest on Loan) Regulations 2020
The Gazette Order exempts licensed banks or financial institution from payment of income tax for interest derived under the Prihatin Rakyat Economic Stimulus Package (PRIHATIN) moratorium programme. The exemption is refer to interest on loan which is due and payable from 1 April 2020 until 30 September 2020.
Gazette Order P.U. (A) 263
Income Tax (Deduction for Expenses in relation to Listing on Access, Certainty, Efficiency (ACE) Market or Leading Entrepreneur Accelerator Platform (LEAP) Market of Bursa Malaysia Securities Berhad) Rules 2020
In conjunction with Budget 2020, tax deduction of up to RM1.5 million be given to the specific listing costs for technology-based companies and SMEs that seek to list their shares in the ACE Market or LEAP Market. Effective YA 2020 to 2022.
Gazette Order P.U. (A) 267
Income Tax (Automatic Exchange of Financial Account Information) (Amendment) Rules 2020
The Automatic Exchange of Financial Account Information (AEOI) excludes depository account which is dormant that:-
a.With balance not exceeding USD 1000;
b.Account holder has not initiated a transaction with regard to the account or other account for the previous three (3) years;
c.Account holder has not communicated with the Reporting Financial Institution (RFI) or any other account for the previous six (6) years; and
d.In relation to Cash Value Insurance Contract, RFI has not communicated with account holder for the previous six (6) years.








